How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. Mastering drone operation isn’t just about pushing buttons; it’s about understanding the technology, adhering to safety protocols, and unleashing your creative potential. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques and responsible operation.
We’ll explore the intricate components of a drone, delve into essential controls and maneuvers, and guide you through the nuances of camera settings and aerial cinematography. We’ll also address safety regulations and maintenance procedures, ensuring you operate your drone confidently and responsibly. Prepare to take flight!
Drone Components and Terminology

Understanding the different parts of your drone and the associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will cover the key components and provide a glossary of common terms.
Drone Component Functions
Each component plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality.
| Component | Function | Common Issues | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust for lift and maneuverability. | Bent or damaged propellers, imbalance. | Inspect for damage, replace if necessary; balance propellers. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers, providing power for flight. | Motor failure, overheating. | Check motor connections, replace faulty motors; ensure adequate cooling. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone, controlling all aspects of flight. | Firmware issues, sensor malfunctions. | Update firmware, recalibrate sensors; seek professional assistance if needed. |
| Battery | Provides power to all drone components. | Low battery, battery swelling, poor battery health. | Charge the battery, replace if swollen or exhibiting poor performance; use a quality charger. |
| GPS | Provides location data for precise positioning and autonomous flight modes. | Weak GPS signal, GPS drift. | Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky; recalibrate GPS. |
| Camera | Captures photos and videos. | Camera malfunction, poor image quality. | Check camera settings, clean the lens; consider professional repair. |
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with these common terms will enhance your understanding of drone operation.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a constant altitude.
- Attitude Mode: A flight mode where the drone’s orientation is controlled relative to its own axes.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera, ensuring smooth footage.
- Payload: The weight of the camera and any other attachments carried by the drone.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): A function that automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point.
- Firmware: The software that controls the drone’s hardware.
- Throttle: The control input that adjusts the drone’s altitude.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring a safe and successful flight. This section details the necessary steps.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, carefully review this checklist to minimize risks.
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Check the battery level and ensure it’s fully charged.
- Verify the GPS signal strength.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Check local regulations and airspace restrictions.
- Inform others of your flight plan.
Drone Power Up and Calibration
Follow these steps to power up and calibrate your drone correctly.
- Power on the remote controller.
- Power on the drone.
- Wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Calibrate the compass by rotating the drone slowly in a complete circle.
- Perform any necessary IMU calibration as per the drone’s manual.
Pre-Flight Process Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight steps.
(Imagine a flowchart here: Start -> Inspect Drone -> Check Battery -> Check GPS -> Calibrate Compass/IMU -> Check Weather -> Check Regulations -> Inform Others -> Ready for Flight)
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the basic controls is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively.
Basic Control Inputs and Their Effects
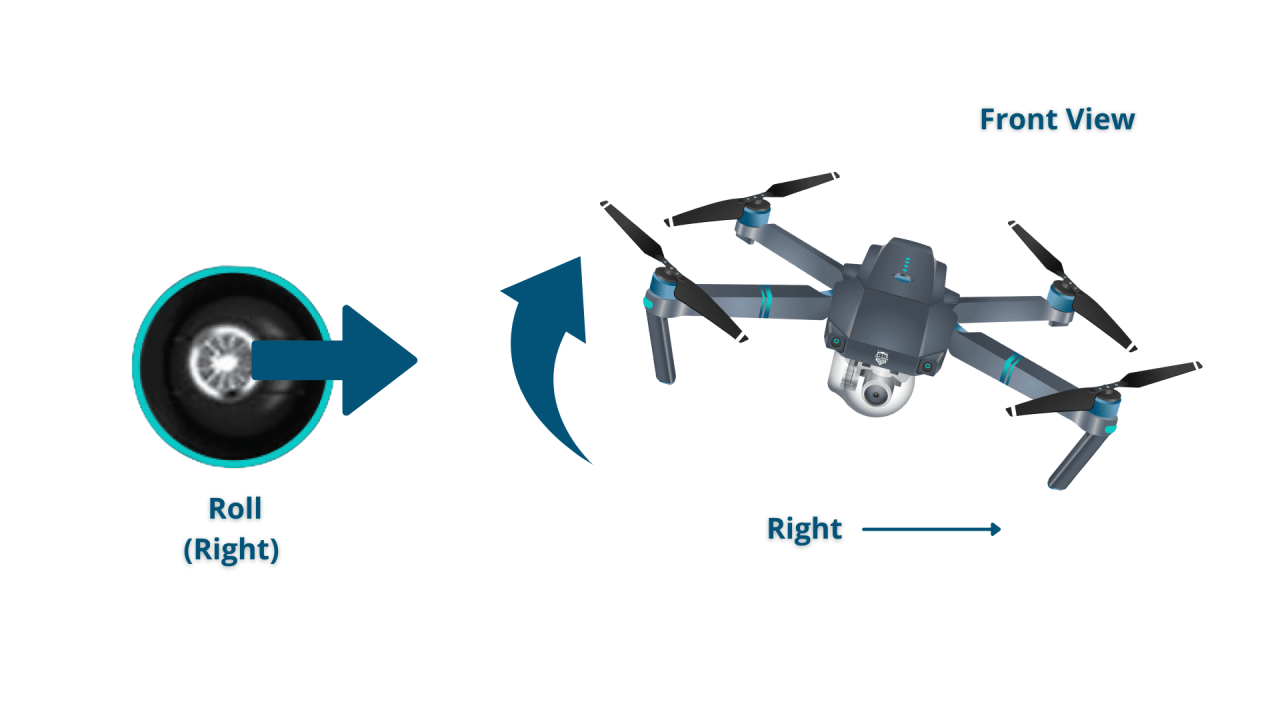
Most drones use two joysticks for controlling movement. One joystick controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the other controls pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right).
- Left Stick (Vertical): Controls altitude (up/down) and yaw (rotation left/right).
- Right Stick (Horizontal): Controls pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right).
- Buttons: Various buttons control functions like takeoff/landing, return-to-home, and camera operation.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Mastering these maneuvers is essential for confident drone piloting.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From there, practice and experience will refine your skills, allowing you to confidently maneuver your drone in various situations.
Mastering the art of drone operation takes dedication, but the rewards are well worth the effort.
- Takeoff: Initiate takeoff using the designated button or joystick input.
- Landing: Initiate landing using the designated button or joystick input.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air using precise joystick control.
- Directional Movement: Control the drone’s movement in any direction using the joysticks.
Common Control Errors and Solutions
Here are some common errors and how to address them.
- Drift: Adjust the trim settings on your controller.
- Uncontrolled Yaw: Recalibrate the compass.
- Difficult Hovering: Practice smooth joystick movements; check wind conditions.
- Unexpected Movements: Check for interference, recalibrate sensors.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore more advanced techniques to enhance your aerial capabilities.
Advanced Maneuvers and Flight Modes
These techniques require practice and a good understanding of your drone’s capabilities.
- Precise Hovering: Requires fine motor skills and consistent joystick control.
- Waypoint Navigation: Plan a flight path using pre-programmed points.
- Filming Techniques: Practice smooth camera movements and various shot types (e.g., orbiting, tracking).
Comparison of Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability.
| Flight Mode | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Relies on GPS for position holding and stability. | Stable shots, autonomous flight. |
| Attitude Mode | Maintains orientation relative to its own axes, ignoring GPS. | Precise maneuvers in confined spaces. |
| Manual Mode | Full manual control, no assistance from the drone’s systems. | Experienced pilots, advanced maneuvers. |
Drone Camera Operation and Settings: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding your drone’s camera settings is crucial for capturing high-quality footage.
Camera Settings and Their Effects
Adjusting these settings allows you to optimize your footage for different scenarios.
- Resolution: Higher resolution means larger file sizes but better image quality (e.g., 4K, 1080p).
- Frame Rate: Higher frame rates result in smoother video (e.g., 60fps, 30fps).
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light; higher ISO is better in low light but can introduce noise.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the lens; affects depth of field.
Optimizing Camera Settings for Lighting Conditions
Adjust settings based on the ambient light.
- Bright Sunlight: Lower ISO, adjust aperture for desired depth of field.
- Overcast Conditions: Slightly higher ISO, may need to increase exposure.
- Low Light: Higher ISO, but be mindful of increased noise.
Camera Shot Examples, How to operate a drone
Different shots offer various perspectives and storytelling capabilities.
- Wide Shot: Shows a broad view of the scene.
- Medium Shot: Shows more detail while still providing context.
- Close-up Shot: Highlights specific details or subjects.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safety and adherence to regulations are paramount when operating a drone.
Potential Hazards and Safety Measures
Understanding potential risks and taking preventative measures is crucial.
- Propeller Strikes: Keep a safe distance from people and objects.
- Loss of Control: Regularly check battery levels and GPS signal.
- Collisions: Maintain visual line of sight and avoid obstacles.
- Malfunctions: Regularly inspect and maintain your drone.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Always check and comply with local laws and regulations before flying.
(Note: Specific regulations vary by location. Consult your local aviation authority for detailed information.)
Best Practices for Responsible Drone Operation
Follow these best practices to ensure safe and responsible drone operation.
- Always maintain visual line of sight.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respect people’s privacy.
- Fly responsibly and consider the environment.
- Register your drone if required by local regulations.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are key to extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its reliable performance.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Implement a routine maintenance schedule to keep your drone in optimal condition.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the drone’s body and propellers.
- Battery Care: Store batteries properly and avoid extreme temperatures.
- Firmware Updates: Keep the drone’s firmware up-to-date.
- Inspections: Regularly inspect for any damage or wear and tear.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Here are some common issues and their potential solutions.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Failure | Faulty motor, loose connection. | Inspect motor and connections; replace if necessary. |
| GPS Issues | Weak signal, interference. | Fly in an open area; recalibrate GPS. |
| Low Battery | Battery discharge, faulty battery. | Charge battery; replace if necessary. |
Drone Photography and Videography Techniques
This section explores techniques for capturing stunning aerial photos and videos.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
These techniques will elevate your aerial photography and videography.
- Lighting: Utilize the “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting.
- Composition: Employ the rule of thirds and leading lines for visually appealing shots.
- Camera Movement: Practice smooth, deliberate camera movements to avoid shaky footage.
- Post-Processing: Utilize editing software to enhance your photos and videos.
Creative Aerial Shots and Compositions
Experiment with different angles and perspectives to create unique and captivating visuals.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety protocols and legal considerations, I recommend checking out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help ensure you operate your drone responsibly and effectively.
- Aerial Panoramas: Capture wide, sweeping views of landscapes.
- Drone Orbits: Create dynamic shots by circling around a subject.
- Tracking Shots: Follow a moving subject from above.
Enhancing Storytelling with Camera Angles
Different camera angles can significantly impact the narrative of your aerial media.
- High Angle Shots: Show the subject from above, creating a sense of scale and perspective.
- Low Angle Shots: Show the subject from below, emphasizing its size and power.
- Unique Perspectives: Experiment with unusual angles to create dramatic and memorable shots.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle unexpected situations is crucial for safe drone operation.
Handling Unexpected Situations

Prepare for potential emergencies to ensure a safe outcome.
- Low Battery Warning: Immediately initiate a return-to-home procedure.
- Loss of Signal: The drone should automatically return to its takeoff point (if RTH is enabled).
- Crashes: Assess the damage and take appropriate action; consider professional repair.
Safely Recovering a Drone
Depending on the scenario, different recovery methods may be necessary.
- Minor Crashes: Inspect for damage, repair if possible.
- Significant Damage: Seek professional repair or replacement.
- Lost Drone: Utilize the drone’s tracking features (if available); contact local authorities if necessary.
Emergency Contact Numbers and Resources
Have a list of emergency contacts readily available.
- Local Emergency Services: (Insert local emergency number)
- Drone Manufacturer Support: (Insert manufacturer contact information)
- Local Aviation Authority: (Insert local aviation authority contact information)
Operating a drone successfully requires a blend of technical understanding and responsible practice. From understanding basic controls to mastering advanced techniques and adhering to safety regulations, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge to embark on your aerial adventures. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and safe drone pilot. Embrace the skies responsibly, and capture stunning visuals that will leave a lasting impression.
FAQ Compilation
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functions. Look for models with intuitive controls and comprehensive tutorials.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, flight conditions (wind, temperature), and usage (camera operation, flight style). Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” function that will automatically guide the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. If this fails, consult your drone’s manual for specific emergency procedures.
Is drone insurance necessary?
Drone insurance is highly recommended, especially for recreational and commercial use. It can protect you from liability in case of accidents or damage.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration processes.
